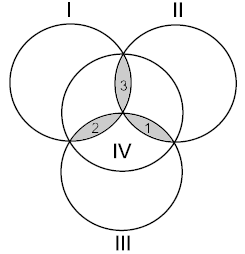
Let us consider four disks intersecting as in the figure. Each of the three shapes formed by the intersection of three disks will be called apetal.
Write zero or one on each of the disks. Then write on each petal the remainder in the division by two of the sum of integers on the disks that contain this petal. For example, if there were the integers
0, 1, 0, and 1 written on the disks, then the integers written on the petals will be 0, 1, and 0 (the disks and petals are given in the order shown in the figure).
This scheme is called aHamming code. It has an interesting property: if you enemy changes secretely any of the seven integers, you can determine uniquely which integer has been changed. Solve
this problem and you will know how this can be done.
Input
The only line contains seven integers separated with a space, each of them being zero or one. The first four integers are those written on the disks in the order shown in the figure. The following three
integers are those written on the petals in the order shown in the figure
Output
Output one line containing seven integers separated with a space. The integers must form a Hamming code. The set of integers may differ from the input set by one integer at most. It is guaranteed that
either the input set is a Hamming code or a Hamming code can be obtained from it by changing exactly one integer.
Samples
input
output
0 1 0 1 1 0 1
|
0 1 0 0 1 0 1
|
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
|
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
|
这样的题目就是考理解题目的能力了。
因为数据十分小,所以使用上面方法都不会超时的,只要答案对就可以了。
所以遇上这样的题目就暴力吧。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void countHammingCode(int B[])
{
B[4] = (B[1] + B[2] + B[3])%2;
B[5] = (B[0] + B[2] + B[3])%2;
B[6] = (B[0] + B[1] + B[3])%2;
}
void HammingCode()
{
int A[7], B[7];
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
{
cin>>A[i];
B[i] = A[i];
}
bool ok = false;
for (int k = -1; k < 4; k++)
{
if (-1 != k) B[k] = !B[k];
countHammingCode(B);
ok = true;
for (int i = 4; i < 7; i++)
{
if (A[i] != B[i]) ok = false;
}
if (ok)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
{
cout<<B[i]<<' ';
}
break;
}
if (-1 != k) B[k] = !B[k];
}
if (!ok)
{
countHammingCode(B);
for (int i = 4; i < 7; i++)
{
A[i] = !A[i];
ok = true;
for (int j = 4; j < 7; j++)
{
if (A[j] != B[j]) ok = false;
}
if (ok)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 7; j++)
{
cout<<B[j]<<' ';
}
break;
}
A[i] = !A[i];
}
}
}
int main()
{
HammingCode();
return 0;
}
觉得上面代码不够简洁的,可以参考下面代码:
void mainHammingCode()
{
int i,m[8];
for(i=1; i<8; i++) scanf("%d", &m[i]);
for(i=1; i<9; i++)
{
if( (m[2]+m[3]+m[4])%2 == m[5] &&
(m[1]+m[3]+m[4])%2 == m[6] &&
(m[1]+m[2]+m[4])%2 == m[7]) break;
m[i]=(!m[i]);
m[i-1]=(!m[i-1]);
}
for(i=1;i<8;i++) printf("%d ",m[i]);
}
分享到:










相关推荐
hamming code in matlab
verilog 实现的hamming码生成,用于fpga
Hamming Code Test Code.
FPGA实现扩展的海明校验码,本程序用于冗余存储器的校验
(7,4)汉明码的硬判决译码算法、最大似然译码算法、和积译码算法性能比较(代码附在word后面,采用matlab实现)很好的学习资料
Belief propagation to decode Hamming(7,4) Code
rectangular and hamming windows code observation of waveforms and DFT spectra of "aa" and "ee" sounds
Haming Code Simulation (7
Additional parity bit hamming code
error Detecting and Error Correcting Codes By R.W.HAMMING
可对二进制数据进行海明编码海明校验的操作
hamming code simulink by using matlab
基于Matlab的汉明码(Hamming Code)纠错传输以及交织编码(Interleaved coding)仿真.zip 1、该资源内项目代码经过严格调试,下载即用确保可以运行! 2、该资源适合计算机相关专业(如计科、人工智能、大数据、数学、...
计算海明码
程序实现汉明码的编码与译码,与一般程序不同,该程序具有良好的接口
实现其海明码的功能,严格按照海明码的原理来编写的程序。
7,4汉明码的编译码原理,用VHDL语言实现的,需要的请下载
matlab用到的汉宁窗函数,用汉明窗限制的线性系统函数
MATLAB仿真作业。 1.Huffman编码 2.qpsk调制与解调 3.hamming信道编码
海明码c++实现,可实现任意长度的海明编码,visual studio 2008编译环境